Early Signs of Brain Tumours: When Should You See a Doctor?
Brain tumours can be intimidating, but recognising the early signs and seeking timely medical care can make a significant difference in outcomes. Understanding the warning signals, diagnostic options, and treatment pathways empowers patients and their families to take proactive steps.
At Fortis Hospital, Shalimar Bagh, our multidisciplinary team provides advanced neurosurgery care, combining cutting-edge technology with personalised treatment plans to ensure the best possible outcomes.
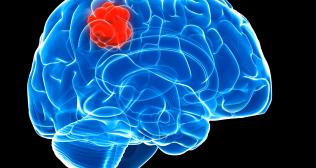
What Is a Brain Tumour?
A brain tumour occurs when cells in the brain grow uncontrollably, forming an abnormal mass. Tumours can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). While some tumours grow slowly and may cause minimal symptoms, others can grow rapidly, affecting brain function and overall health.
Brain tumours can either originate in the brain (primary brain tumours) or spread from other parts of the body (secondary or metastatic tumours). Early recognition and diagnosis are critical for effective management.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Brain Tumours
Recognising brain tumour symptoms early can save lives. While symptoms vary depending on tumour size, location, and growth rate, common warning signs include:
- Persistent Headaches: Headaches that worsen over time or are more severe in the morning.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Especially when accompanied by headaches or dizziness.
- Seizures: Sudden onset seizures in adults may indicate a brain lesion.
- Vision or Hearing Problems: Blurred or double vision, or unexplained hearing loss.
- Cognitive Changes: Memory lapses, confusion, or difficulty concentrating.
- Weakness or Numbness: Particularly on one side of the body.
- Speech Difficulties: Trouble forming words or sentences.
- Balance and Coordination Issues: Frequent clumsiness or unsteady gait.
It is important to remember that these symptoms can occur due to several conditions, but if they persist or worsen, immediate medical evaluation is recommended.
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you notice persistent or unusual neurological symptoms, consult a healthcare professional promptly. Early evaluation increases the chances of identifying brain tumours at a stage when treatment is more effective.
A neurosurgeon can perform a detailed assessment, order diagnostic tests, and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan.
Diagnostic Tests for Brain Tumours
Once symptoms suggest the possibility of a brain tumour, specialists may recommend several tests:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): The most precise imaging technique for detecting brain tumours.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Useful for rapid evaluation or in emergency situations.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan: Pet is usually reserved for secondary brain tumors that are spread from other cancer in the body.
- Biopsy: Tissue sampling may be performed to confirm tumour type and guide treatment.
At Fortis Hospital, Shalimar Bagh, advanced imaging ensures accurate diagnosis, helping neurosurgeons plan precise interventions.
Treatment Options for Brain Tumours
Treatment depends on tumour type, size, location, and overall patient health. Modern brain tumour treatment options include:
1. Surgery
Surgery aims to:
- Remove as much of the tumour as can be done safely
- Reduce pressure on surrounding brain tissue
- Obtain tissue for diagnosis
Minimally invasive techniques, including keyhole and robotic-assisted surgery, are used when feasible to minimise complications and shorten recovery time.
2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to destroy tumour cells. It can be employed:
- After surgery to eliminate residual cells
- As the primary treatment when surgery is not possible
- For palliative care to relieve symptoms
Advanced techniques such as stereotactic radiosurgery precisely target tumours while sparing healthy brain tissue.
3. Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy
Chemotherapy targets rapidly dividing tumour cells, while targeted therapy focuses on specific molecules or pathways involved in tumour growth. These approaches are personalised based on tumour type and genetic profile to maximise effectiveness and reduce side effects.
4. Immunotherapy
Emerging immunotherapies help the body’s immune system fight tumour cells. While still evolving, this approach is promising for certain malignant brain tumours.
5. Multidisciplinary Care
Effective treatment often involves a team-based approach:
- Neurosurgeons for surgical care
- Oncologists for chemotherapy or radiation guidance
- Neurologists for symptom management
- Physiotherapists and occupational therapists for rehabilitation
- Nutritionists for dietary support during recovery
At Fortis Hospital, Shalimar Bagh, this integrated model ensures patients receive comprehensive care from diagnosis through recovery.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery depends on tumour type, treatment method, and overall health. Rehabilitation may include:
- Physiotherapy: To regain strength, balance, and coordination
- Occupational Therapy: For daily living activities and fine motor skills
- Speech Therapy: For patients experiencing speech or swallowing difficulties
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: Exercises to improve memory, attention, and problem-solving skills
Regular follow-up and imaging are essential to monitor recovery and detect any recurrence early.
Lifestyle and Supportive Care
Alongside medical treatment, supportive care can improve outcomes:
- Balanced Nutrition: Supports healing and immune function
- Stress Management: Counselling, meditation, or support groups
- Physical Activity: Helps maintain strength and mental wellbeing
- Family and Community Support: Emotional wellbeing is key to recovery
Fortis provides patient support programmes to guide both patients and families through the treatment journey.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. Can brain tumours be completely cured?
Some tumours, particularly benign ones, can be entirely removed. Malignant tumours may require surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Early detection improves treatment success.
Q. How do I know if my headaches are serious?
Persistent or worsening headaches, especially with nausea, vision changes, or weakness, should be evaluated promptly. Imaging is the only way to confirm the cause.
Q. Is neurosurgery safe?
Yes. With modern imaging, minimally invasive, and robotic-assisted techniques, neurosurgery is highly precise and safe. Expert teams at Fortis ensure optimal outcomes.
Q. What is the difference between benign and malignant tumours?
Benign brain tumours do not spread to other parts of the body and tend to grow slowly. Malignant tumours, on the other hand, can grow more rapidly and invade nearby brain tissue. However, unlike many other cancers, brain tumours—whether benign or malignant—usually do not spread to other organs.
Conclusion
Recognising early signs of brain tumours and seeking prompt medical attention is vital for successful treatment. With modern brain tumour treatment options — including surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and emerging therapies — patients can achieve improved outcomes and better quality of life.
At Fortis Hospital, Shalimar Bagh, our expert neurosurgery team provides personalised, multidisciplinary care, guiding patients through every step of diagnosis, treatment, and recovery.
If you or a loved one notice persistent headaches, seizures, or other neurological changes, consult our specialists immediately. Early action can make all the difference.
Categories
Clear allMeet the doctor

- Neurosurgery | Neurosurgery | Neuro and Spine Surgery
-
28 Years
-
1500