Recognizing Early Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment of Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a bacterial infection of deeper skin layers. Lower body parts are commonly affected by cellulitis, but it can also affect any body part, such as the face, arms, and other areas. Cellulitis causes the skin to be red and inflamed. If left untreated, it can lead to potentially life-threatening conditions as it rapidly spreads through lymph and blood.
Cellulitis causes:
Streptococcus and Staphylococcus bacteria cause cellulitis infections. These bacterial infections are similar to other infections, such as impetigo and erysipelas. However, cellulitis is a deeper bacterial infection involving the deeper skin layers.
Some of the common cellulitis causes include:
- Bacteria can enter the skin from any defect in the skin layers, such as a skin cut, puncture wound, or insect bite. They can also affect the skin around ulcers or surgical wounds.
- Bacteria penetrate the skin layers and affect the deeper tissues by destroying the various layers, such as fascia, dermis, and epidermis.
- Beta-hemolytic streptococci are the bacteria that most commonly cause cellulitis. Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus agalactiae are the most common streptococci.
- Staphylococcus bacteria are another common type that causes cellulitis. Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant S. Aureus are also common bacteria that cause cellulitis.
- Hemophilus influenzae bacteria commonly causes cellulitis of the face, arms, and upper body in children.
- Aeromonas hydrophilia and Vibrio vulnificus cause cellulitis after freshwater or seawater exposure.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa causes cellulitis after a puncture wound.
- Leg swelling that persists for a long time due to conditions such as varicose veins or impaired venous drainage can also cause cellulitis.
- Medical conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and radiation therapy are some of the other cellulitis causes.
Risk factors for cellulitis:
Some of the risk factors for cellulitis include:
Preexisting skin infections such as athlete's foot, fungal infections in the skin creases, and the toes
- Metabolic diseases such as diabetes or poorly controlled human immunodeficiency virus infections compromise the immune system, leading to an increased risk of cellulitis.
- Blood circulatory conditions such as varicose veins, obesity, pregnancy, and previous surgeries also increase the risk of cellulitis.
- Animal bites, injection drug usage, and bed sores increase the risk of cellulitis.
- Superficial viral infections, such as herpes or varicella infections, and fungal infections, such as intertrigo, also increase the risk of cellulitis.
- A previous history of cellulitis or any other skin infections increases the risk of cellulitis.
- Poor circulation in the superficial arteries, veins, or lymph vessels leads to stagnation and can increase the risk of cellulitis.
Cellulitis types:
There are three types of cellulitis based on the area it affects.
- Buccal cellulitis develops on the cheeks of young children due to dental infections.
- Preseptal cellulitis develops in front of the eyes in the eyelids of young children under 5 years old.
- Orbital cellulitis, which develops behind the eye and is less commonly seen, is a relatively more serious infection than other types.
Cellulitis symptoms:
Cellulitis causes specific symptoms in the body. These include:
- Pain, tenderness, swelling, redness that spreads to the underlying tissues
- Warmth feel of the skin
- Enlarging redness
- Red or purple discoloration of the skin that resembles a rash called cellulitis rash
- Fever with chills, sweats, and swollen lymph glands
- Drainage of clear or red-tinged fluid from the skin that may or may not be foul-smelling.
- Pus if staphylococcal infections cause the infection
- One of the conditions that mimics cellulitis is stasis dermatitis, which occurs due to poor circulation in the legs. This may look like cellulitis, but it is not the same.
Interesting things about cellulitis:
- Cellulitis is a widespread infection
- It affects people of all ages and genders
- Middle-aged and older adults are more prone to cellulitis
- Cellulitis is not contagious as it is the infection of deeper layers of skin, and the superficial skin may remain intact.
Cellulitis complications:
Cellulitis complications include bacteremia, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, and sepsis. These infections spread to underlying skin layers and can cause severe infections. Occasionally, they can lead to chronic swelling of the affected body parts.
Cellulitis diagnosis:
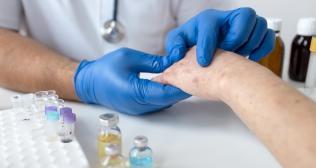
Physical examination followed by specific blood tests help in cellulitis diagnosis.
- A healthcare professional physically examines the area of infection suspected to have cellulitis. They observe the classic signs of redness, swelling, warmth, tenderness, fluid-like discharge, and pus.
- Cellutis tests are recommended to identify if the infection has spread to other body parts. These include:
- Blood tests identify the infection, the amount of infection present, and whether cellulitis has spread throughout the body.
- A skin test identifies the bacteria responsible for cellulitis. This helps identify the appropriate bacteria responsible for infection so that antibiotics can be prescribed accordingly.
- Bacterial culture also identifies the bacteria responsible for cellulitis.
Cellulitis treatment:
- Antibiotics are the mainstay of cellulitis treatment. The healthcare provider (HCP) prescribes antibiotics for at least 5-10 days, and the full course must be completed. The HCP should be informed if the cellulitis is responding or not.
- Cellulitis treatment varies based on the response. If the symptoms do not subside, are extensive, or there is a high fever, then an individual has to be hospitalized for further investigation, and intravenous antibiotics have to be given.
- Warm compression can be done to reduce swelling and infections. The affected area should be elevated to improve the blood flow to the affected area. Compression stockings or wraps can improve blood flow. They should be removed twice daily for 10-15 minutes. However, if cellulitis is not completely treated, cellulitis removal surgery is recommended.
Cellulitis prevention:
Some of the preventive steps for cellulitis infection include:
- Use soap and water to Wash the wound regularly. This has to be done gently as part of the bathing routine.
- The HCP may prescribe protective antibiotic cream or ointment. Sometimes, nonprescription ointments such as Vaseline or Polysporin also provide adequate protection from outside exposure.
- A bandage should cover the wound, and the dressing has to be changed daily.
- Monitor the signs of infection, such as irritation, pain, and pus, for possible need for additional medical support.
Extra care has to be taken by people with diabetes and those with poor venous or arterial circulation. This includes:
- The feet should be regularly inspected for fungal infections or injuries to prevent cellulitis.
- Apply skin moisturizers regularly and lubricate the skin to prevent cracking and peeling. Moisturizing your skin regularly.
- Finger and toenails have to be regularly trimmed to prevent injury to the surrounding skin.
- Hands and feet have to be protected by wearing suitable footwear and gloves.
- Protecting your hands and feet by wearing footwear and gloves.
- Visit a healthcare professional to get the correct treatment for athletes' feet or other skin infections.
Conclusion:
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection caused by streptococcal and staphylococcal bacteria. Symptoms range from pain, swelling, fever, and warmth to redness called a cellulitis rash. Antibiotics are the mainstay of cellulitis treatment.